冒泡排序算法[动图介绍]
更新时间:2019年11月20日14时13分 来源:传智播客 浏览次数:
冒泡排序算法思想:
让数组中的两个相邻数字进行比较,数组中较大的值向下沉,值小的上浮,就类似于水中的气泡,较大的下沉,较小的上升,慢慢冒出来。简单的说就是数值大的会慢慢往前排,数据值小的会慢慢向后排,最终实现由小到达排列,最小的排在最前,最大的排到最后。
冒泡排序图解:
==================================
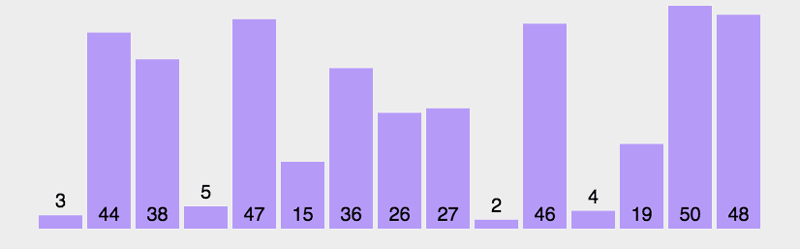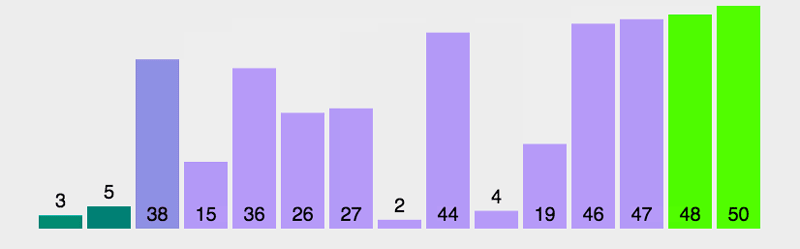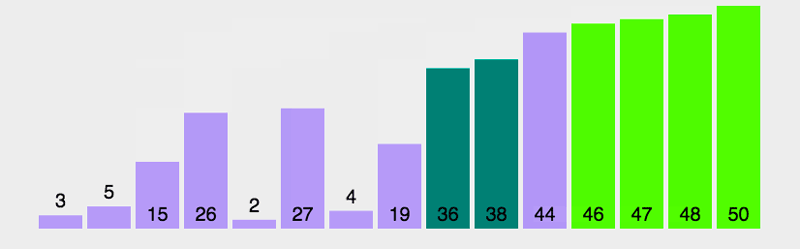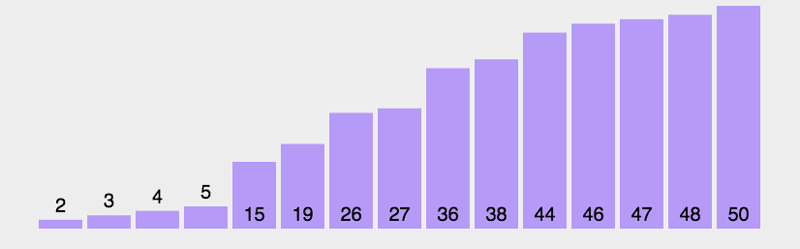
算法执行前
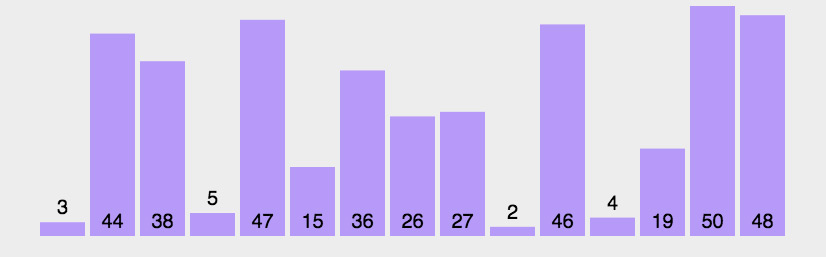
=================================
算法执行后
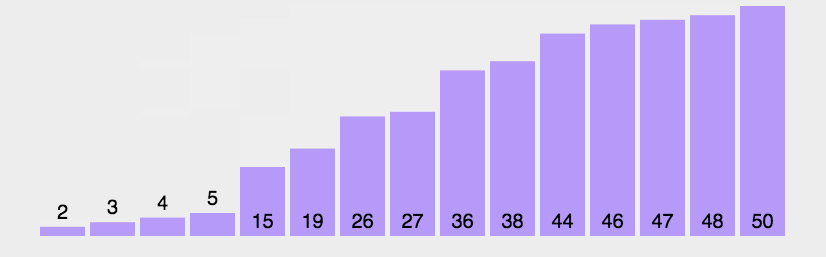
====================================
冒泡算法执行过程【动图版】
冒泡排序算法JAVA实现代码
import com.jiajia.ArrayUtil.*; // 按包名导入
public class BubbleSortMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3,43,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,44,4,50,19,38};
bubbleSort(arr);
ArrayUtil.print(arr);
}
/**
* 冒泡排序
*/
private static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - i -1; j++) { // 这里说明为什么需要-1
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
冒泡排序算法python实现代码
def bubble_sort(the_list):
i = 0
while i < len(the_list):
j = 0
while j < len(the_list)-1:
print(the_list[j],the_list[j+1])
if the_list[j] > the_list[j+1]:
the_list[j], the_list[j+1] = the_list[j+1], the_list[j]
j = j+1
print(the_list)
print("======"+str(the_list))
i = i+1
return the_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
the_list = [3, 43, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 44, 4, 50, 19, 38]
print("排序前:" + str(the_list))
print("排序后:" + str(bubble_sort(the_list)))
猜你喜欢:
















 AI智能应用开发
AI智能应用开发 AI大模型开发(Python)
AI大模型开发(Python) AI鸿蒙开发
AI鸿蒙开发 AI嵌入式+机器人开发
AI嵌入式+机器人开发 AI大数据开发
AI大数据开发  AI运维
AI运维 AI测试
AI测试 跨境电商运营
跨境电商运营 AI设计
AI设计 AI视频创作与直播运营
AI视频创作与直播运营 微短剧拍摄剪辑
微短剧拍摄剪辑 C/C++
C/C++ 狂野架构师
狂野架构师